Varicose veins, those twisted, enlarged veins often seen on the legs, can be more than just a cosmetic concern. While many people seek treatment for their appearance, it’s essential to understand the diagnostic process and the role of medical professionals in addressing this vascular issue. From understanding the symptoms to identifying the right specialist, let’s embark on a journey through the diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins.
Understanding Varicose Veins:
Varicose veins are a common vascular condition characterized by swollen, twisted veins that are often visible just beneath the skin’s surface. They typically occur in the legs and can be caused by weakened or damaged valves within the veins, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure. Symptoms of varicose veins may include visible veins, swelling, aching, heaviness, and discomfort, particularly after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Diagnostic Process:
Diagnosing varicose veins involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically starting with a thorough medical history and physical examination. During the physical exam, the what doctor treats varicose veins will assess the appearance of the veins, inquire about symptoms, and evaluate risk factors such as age, family history, and occupation. While the physical examination provides valuable insights, additional tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Diagnostic Tests:
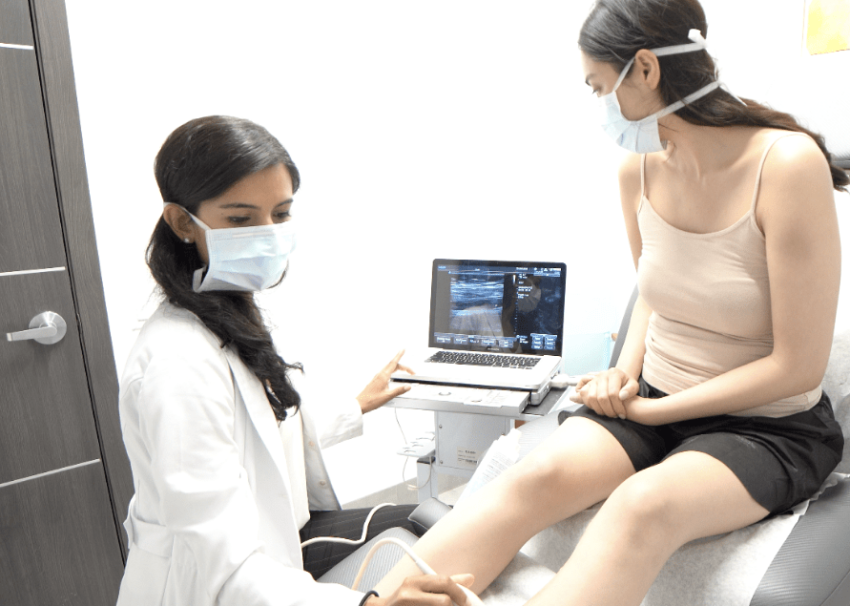
Duplex Ultrasound:
Duplex ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that allows doctors to visualize the veins in the legs and assess blood flow. By combining traditional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound, this imaging technique provides detailed images of the veins’ structure and function, helping doctors identify abnormalities such as blood clots, valve dysfunction, and reflux.
Venous Reflux Exam:
Venous reflux exams, also known as venous Doppler studies, focus on evaluating the function of the valves within the veins. During this test, ultrasound technology is used to measure the direction and speed of blood flow, helping identify areas of reflux where blood flows backward due to valve incompetence. Venous reflux exams are particularly useful in diagnosing chronic venous insufficiency, a condition commonly associated with varicose veins.
Venography:
Venography is a more invasive imaging technique that involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins to visualize blood flow using X-ray imaging. While less commonly performed today due to the availability of non-invasive tests like duplex ultrasound, venography may be recommended in certain cases where other diagnostic methods are inconclusive or when detailed imaging is required for treatment planning.
Choosing the Right Specialist:
Once varicose veins are diagnosed, the next step is to determine the appropriate specialist for treatment. While primary care physicians can offer initial evaluation and guidance, specialized care may be necessary for comprehensive management. Several types of healthcare professionals may be involved in the treatment of varicose veins, including:
Vascular Surgeons:
Vascular surgeons are specialists trained in the diagnosis and treatment of vascular conditions, including varicose veins. They have expertise in both surgical and minimally invasive procedures for addressing venous insufficiency and restoring proper blood flow in the affected veins.
Interventional Radiologists:
Interventional radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in performing minimally invasive procedures using imaging guidance. In the context of varicose veins, interventional radiologists may perform procedures such as endovenous ablation or sclerotherapy to treat venous insufficiency and improve symptoms.
Phlebologists: Phlebologists are physicians who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of vein disorders, including varicose veins and spider veins. While not typically considered medical doctors in the traditional sense, phlebologists undergo specialized training in venous medicine and may offer a range of treatment options for patients with venous disease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, diagnosing varicose veins involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include a physical examination and diagnostic tests such as duplex ultrasound and venous reflux exams. Once diagnosed, the appropriate specialist, whether a vascular surgeon, interventional radiologist, or phlebologist, can provide personalized treatment options to address the underlying venous insufficiency and improve symptoms. By understanding the diagnostic process and collaborating with the right healthcare professionals, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing varicose veins and optimizing vascular health.